Hibrix has been conducting industry trials on its product since 2005 overseen by government agencies, independent agricultural specialists and leading industry participants.
Hibrix trials have been conducted across most major agricultural sectors including the wheat, sugar cane, maize and pasture industries. The results unify to show that agricultural applications of the Hibrix brand can yield results 18- 34 % greater than untreated Hibrix crops in the controlled study.
Other informal industry testing replicate the results with barley, oats, hay varieties, fruit crops, including apples, apricots and peaches, nut varieties, and potatoes to name a few.
Soil Additive Trial – Mackays Warrami (2015)
Aims:
To determine if the rate of Nitrogen and
Photosphirs can be altered when using a soil
additive products
To compare standard fertilser at Six Easy Steps
rates to a new Fertilser product ( Stoller)
Pasture Trial – Waroona (2015/2016)
Dry matter production in the second year of pasture trials in Waroona have been outstanding, unfortunately Waroona suffered terribly during the recent bush fires.
Pasture Production Results
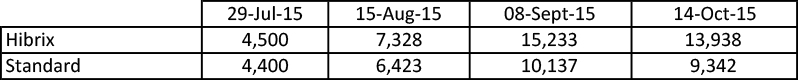

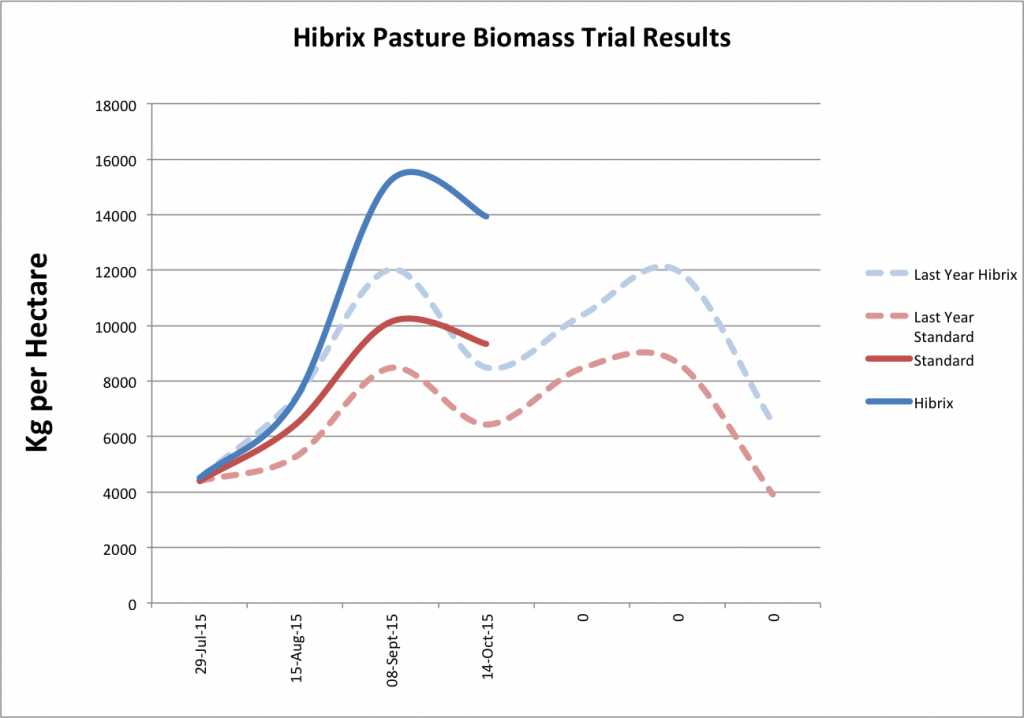
Pasture Trial – Waroona (2014/2015)
At Waroona in the Peel region of Western Australia in 2014, 12 by 1m square wire cattle cages were placed at random to evaluate the effects of Hibrix pasture treatment combined with 50kg/ha of super phosphate versus the growers standard fertiliser usage of 100kg/ha of super phosphate.
The Hibrix treated plots produced significantly higher amounts of dry matter without any reduction in pasture quality. On average Hibrix increased the pasture biomass yield by 34% across the farm. The protein content and metabolisable Energy (Mj/kg Dm) were significantly higher in the Hibrix treatments. Full version of the report available.
Wheat Trial Report (2014/2015)
At Northam in the central wheatbelt of Western Australia in 2014, wheat cv. Eradu was sown into a wheat stubble paddock to evaluate the effects of various rates of fertiliser in combination with Hibrix BB. Agras fertiliser was banded below the seed at sowing at 0, 25, 51, 75 or 99 kg/ha whilst Hibrix BB was applied to half of each plot as a broadcast soil spray at 2.5 L/ha two days after sowing.
The untreated control (no Hibrix BB or Agras) yielded 1.67 t/ha. Increases ranged from 6% to 39%. The Agras only treatments increased overall yields by 7.3%. The Agras plus Hibrix treatments increased overall yields by 17.9%.
The standard farming practice of full rate Agras (99 kg/ha) without Hibrix yielded 1.833 t/ha which was 16.7% greater than the untreated control. In comparison, half rate Agras (51 kg/ha) plus Hibrix yielded 1.992 t/ha which was 18.2% greater than the untreated control.
2014 Soyabean Trial
Results of studies carried out under growth room conditions indicated that Hibrix soil amendment can provide significant increases in the growth of wheat, soybean and canola. In the summer of 2013, a field trial was conducted using soybeans as the indicator crop to test the effectiveness of Hibrix soil amendment for increasing plant growth and productivity under field conditions. The trial was laid out in a randomized block design with 4 replicates. Plots were planted in 7 rows on 50 cm row spacing to a length of 10M with a 7 row John Deere plot planter. Plots measured 3.5m x 8m. The treatments were applied to a length of 10M and alleys were rototilled out to give a final plot length of 8m (Table 1). The soil applied treatment at 2.5 l/ha and the soil/foliar applied treatment had the highest yields of the 4 treatments (Figure 4). All Hibrix treatments had significantly higher yields than the control plot.
Corn Production in the Bowen Food Basin
In Bowen, Queensland, in 2010, Hibrix was compared with a high NPK mineral fertiliser program for the production of maize cv. Hycorn 675IT on an alluvial sandy loam soil irrigated via sub-surface drip tape. At commercial harvest, cobs from 20 randomly selected plants per plot from were harvested, weighed and the length, girth at the cob base and length of tip not filled with kernels was measured. The grain was removed from each cob and weighed. A subsample of 100 grains was selected from the grain from each cob and weighed to determine mean grain size per cob. HibrixBB at 2.5 L/ha applied at sowing in conjunction with the use of a pre-emergent herbicide produced a commercially acceptable maize crop.
The nutrient input costs of Hibrix is less than 20% of your current fertiliser.
Northam Wheat Trial – NPK Reduction
First of a five year trial producing wheat at reduced rates of NPK (50% to 75%). At Northam in the central wheatbelt of Western Australia in 2013, wheat cv. Eradu was sown into a pasture paddock to evaluate the effects of various rates of fertiliser in combination with Hibrix BB. Agras fertiliser was banded below the seed at sowing at 0, 25, 51, 75 or 99 kg/ha whilst Hibrix BB was applied to half the plots as a broadcast soil spray at 2.5 L/ha two days after sowing. There were no visual differences in crop establishment or biomass between treatments. Hibrix BB showed numerically higher NDVI readings compared to the same rate of Agras applied alone. At equivalent rates of Agras, the addition of Hibrix consistently showed numerically higher yield. The second year (2014) is progressing much as expected.
The standard farming practice of full rate Agras (99 kg/ha) without Hibrix yielded 1.833 t/ha which was 16.7% greater than the untreated control. In comparison, half rate Agras (51 kg/ha) plus Hibrix yielded 1.992 t/ha which was 18.2% greater than the untreated control.
Wheat Trial in Narembeen
Average wheat head was larger Average number of grains per head increased Average weight of each grain increased Input costs were reduced.





